Robot programming lecture note
기말 정리 Robot Programming
10. To understand SLAM
Localization
- 2장의 사진이 있을 때, 실제 location 이나 trajectory를 알 수 있는가?
- 실제 지도가 있고, 카메라 intrinsic parameter를 알면 알 수 있음.
Mapping
- 2장의 사진을 통해 Map을 만들 수 있는가?
- 나의 정확한 pose와 카메라 intrinsic parameter를 알면 알 수 있음.
Feature points
- Feature
- Salient and repeatable points or regions
- Requirements
- 다른 이미지에서 같은 point가 비슷한 feature를 가지고 있어야함.
- 뷰 포인트가 변경 되어도 동일한 위치에서 발견되어야 함.
- Rotation invariant
- Scale invariant
- Feature extraction method
- Point-based methods
- Harris Corner
- Fast
- Blob-based methods
- DOF(Different of Gaussian)
- LoG(Laplacian of Gaussian)
- Region-based methods
- MSER(Maximally stable extremal regions)
- Point-based methods
- Feature Matching
- Template matching
- Template: 2D matrix centered on point
- Window를 통해 비교를 하여 matching
- SAD: Sum of Absolute Differences
- SSD: Sum of Squared Differences
- NCC: Normalized Cross Correlation
- SSD가 SAD에 비해 outlier에 덜 민감함.
- robust하지 않음.
- Feature matching
- descriptor → matching
- Discriptor
- Feature point에 대한 설명
- ex) SIFT, ORF, SURF
- Template matching
Localization & Mapping
- Mapping
- feautre extraction & matching
- back proejection
- 정확하게 카메라의 ray가 어디서 오는지 모르지만 카메라의 방향은 알기 때문에, 카메라에서 각 점을 이은 선이 한점에서 만나는 점을 찾는다. 해당 점은 실제 feature가 있던 위치.
- Localization
- Data association
- Pose estimation
- 실제 물체의 position, intrinsic parameter, 2D position을 알면 카메라의 Rotation, Translation을 알 수 있음.
11. Introduction to SLAM
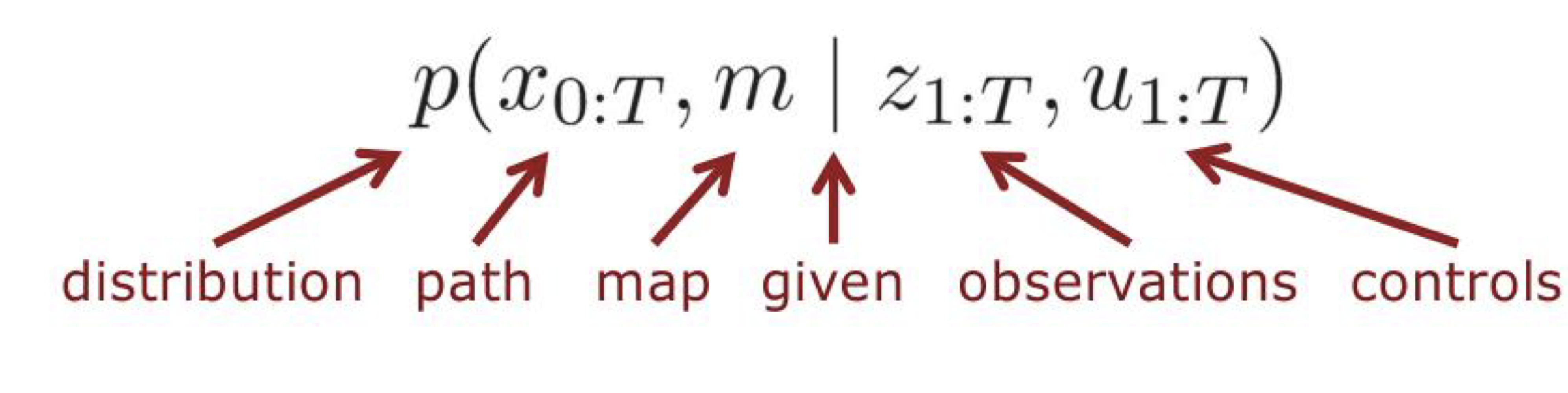
SLAM
- Simultaneously localization and mapping
- Given Data
- The robot’s controls (로봇 제어)
- Observation
- Wanted
- Map of the environment
- Path of the robot
- Probabilistic Approaches’
- Given data 또한 완벽하게 정확하지 않음.
- 따라서 확률 사용.
- Full SLAM vs Online SLAM
- Full SLAM estimates the entire path
- Online SLAM estimates only the latest pose
- Motion model
- Described the relative motion of the robot
- 이전 pose 와 control을 알 때, 어떠한 pose를 취하고 있는지
- Gausian Model, Non-Gaussian Model
- Observation mdoel
- measurements with the robot’s pose
- Gaussian Model, Non-Gaussian model
12. Probabilistic Robotics
Marginalization
- 원하는 변수는 제외하고 다 더해서 원하는 변수만 남겨 놓는 것.
Bayes Formula
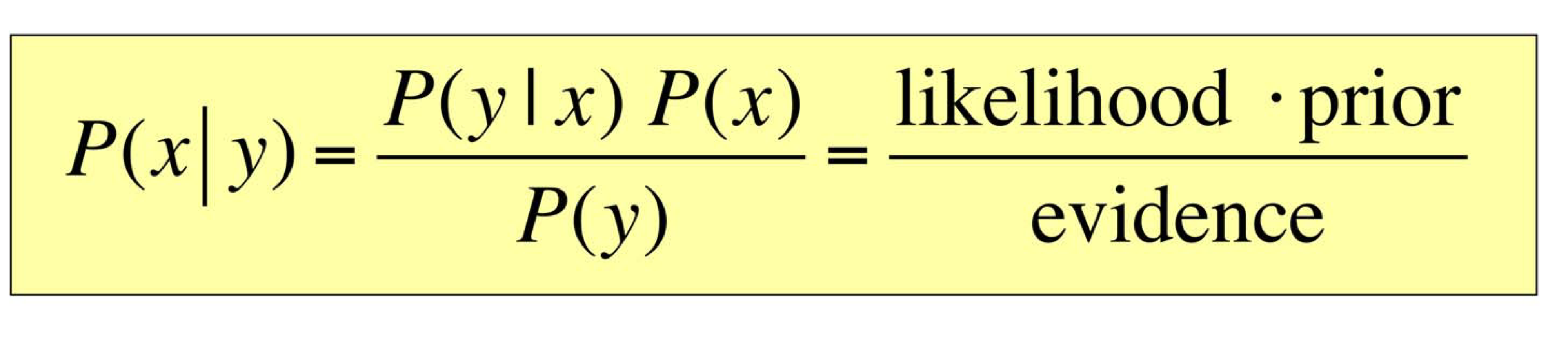
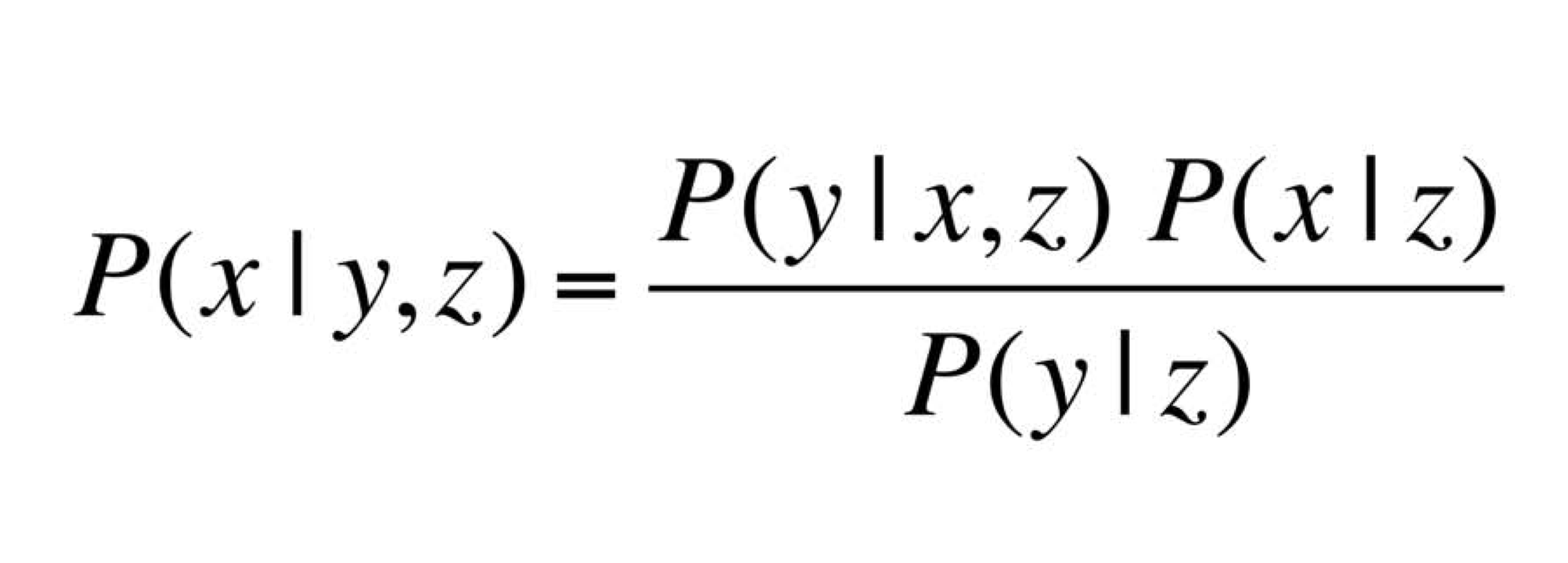
Causal vs Diagnostic Reasoning
- Diagnostic
-
P(open z), 즉, 어떤 상황에서 해당 사건이 일어났을 확률
-
- Causal
-
p(z open), 어떤 사건이 일어났을 때, 어떤 상황인 경우 - 주로 Causal이 얻기 쉬움
-
Recursive Bayesian Updating
- Markov assumption
- 만약 현재 상태가 이전 상태와 독립하다고 가정하고 구함.
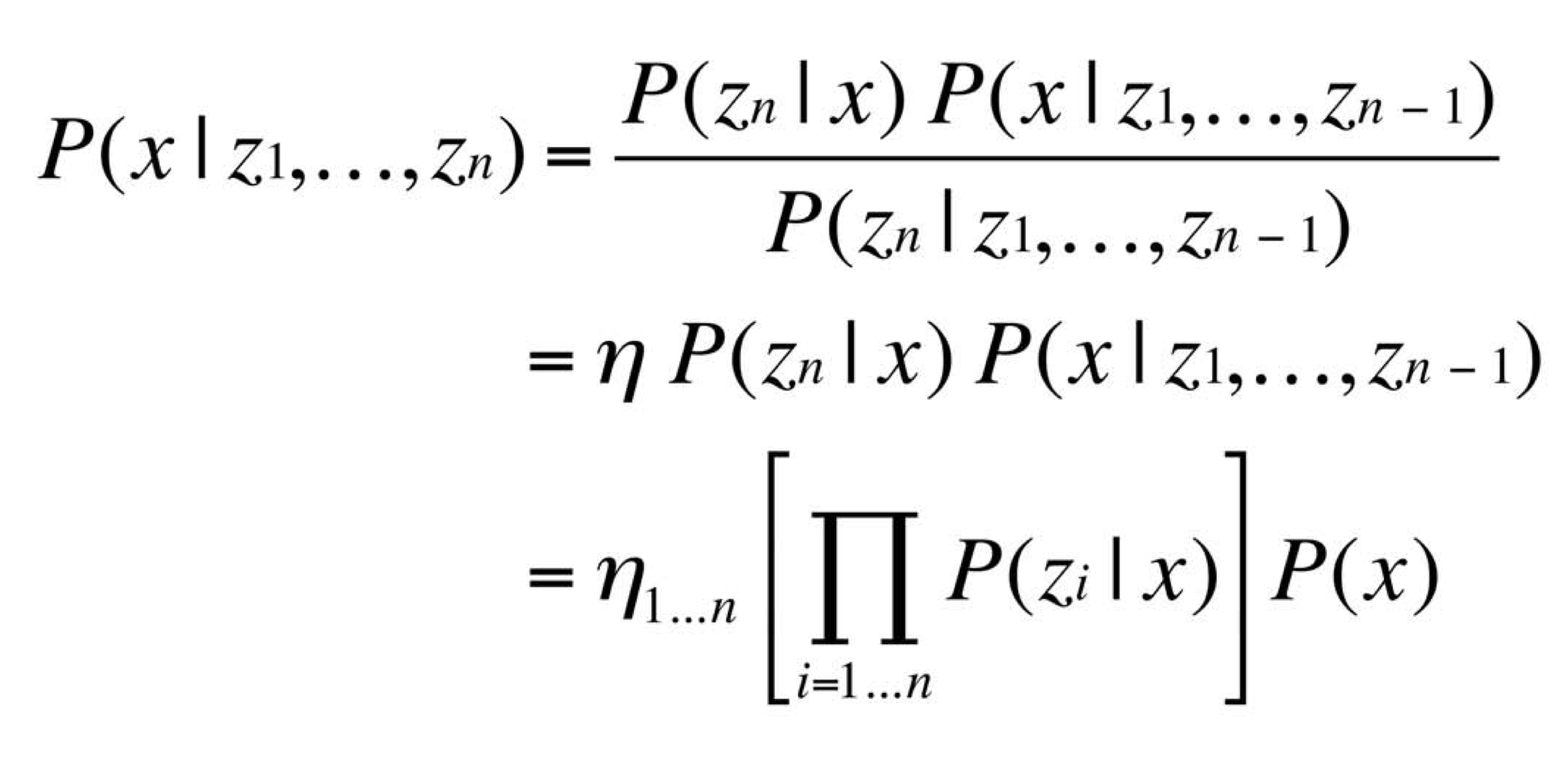
Action
- Action은 절대로 정확하게 원하는대로 수행되지 않음. 따라서 확률을 이용하여 Action을 취했을 때, 다음 State를 예측. Bay
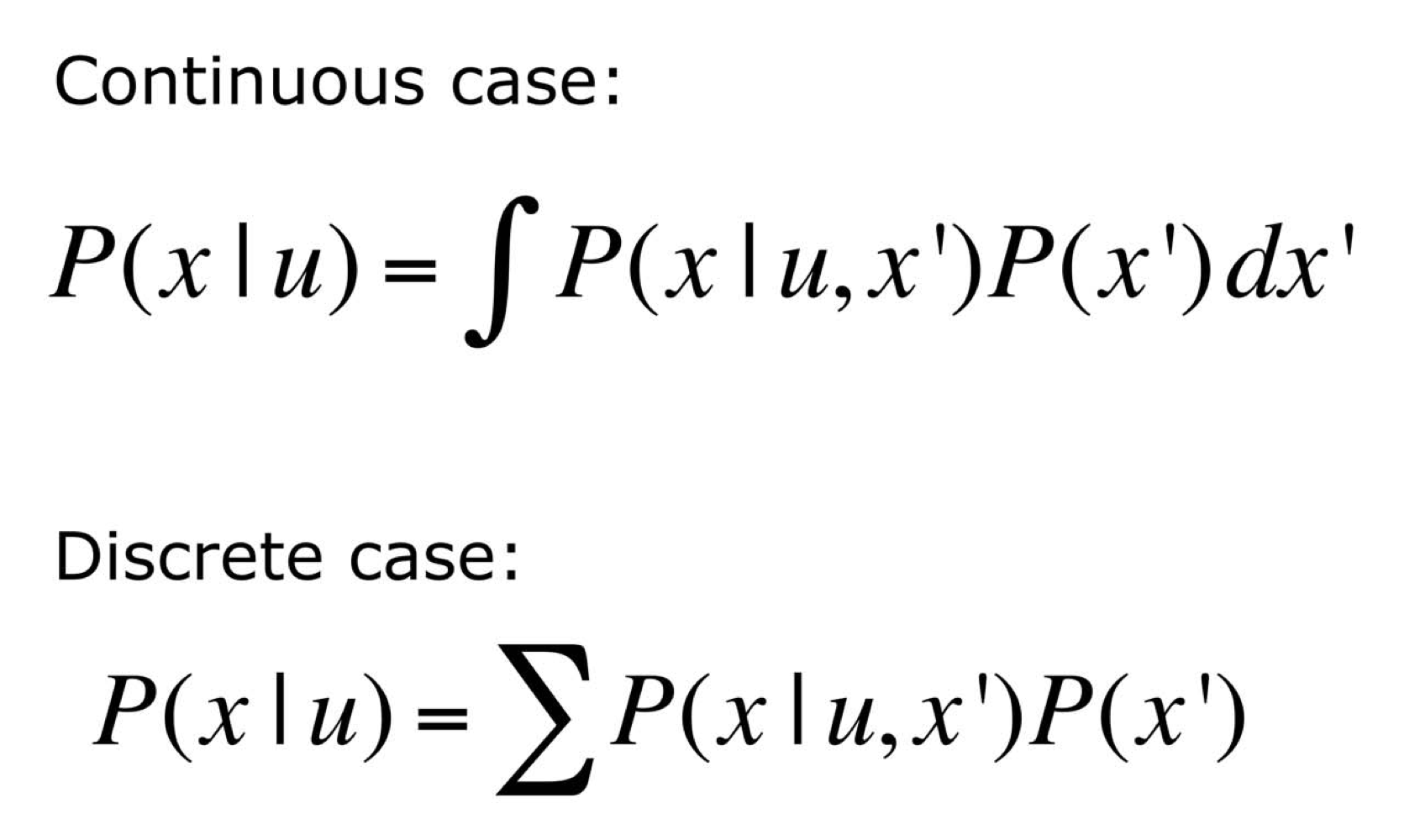
Bayes Filter
- Given: observation, Sensor model, Action model, Prior state
- Wanted: Next state
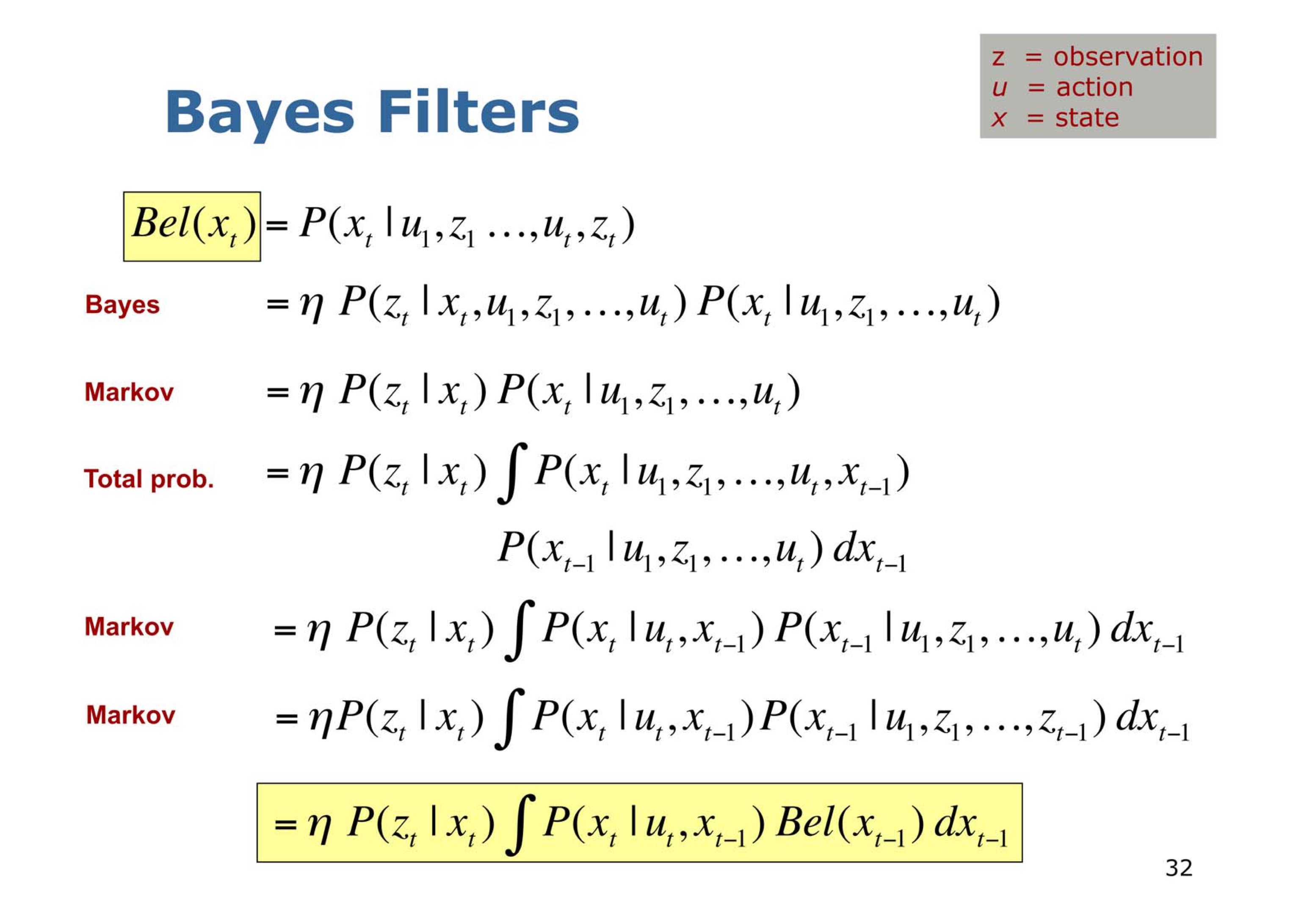
13. Homogeneous Coordinate
Homogeneous Coordinates
- a system of coordinates used in projective geometry(Euclidian geometry)
- Single Matrix can represent affine transformations and projective transformations
- From Homogeneous to Euclidian Coordinates
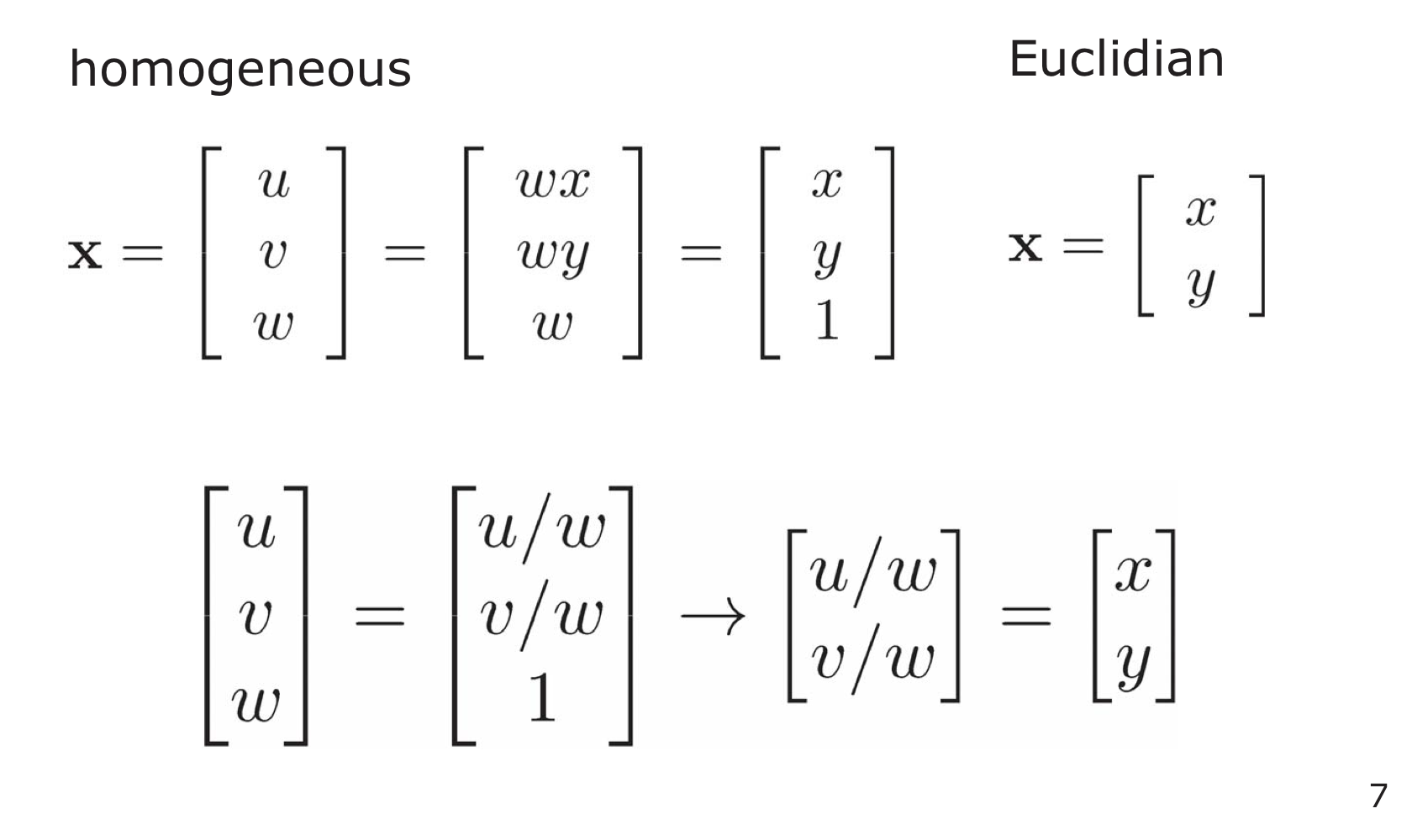
Transformation and Rotation Matric
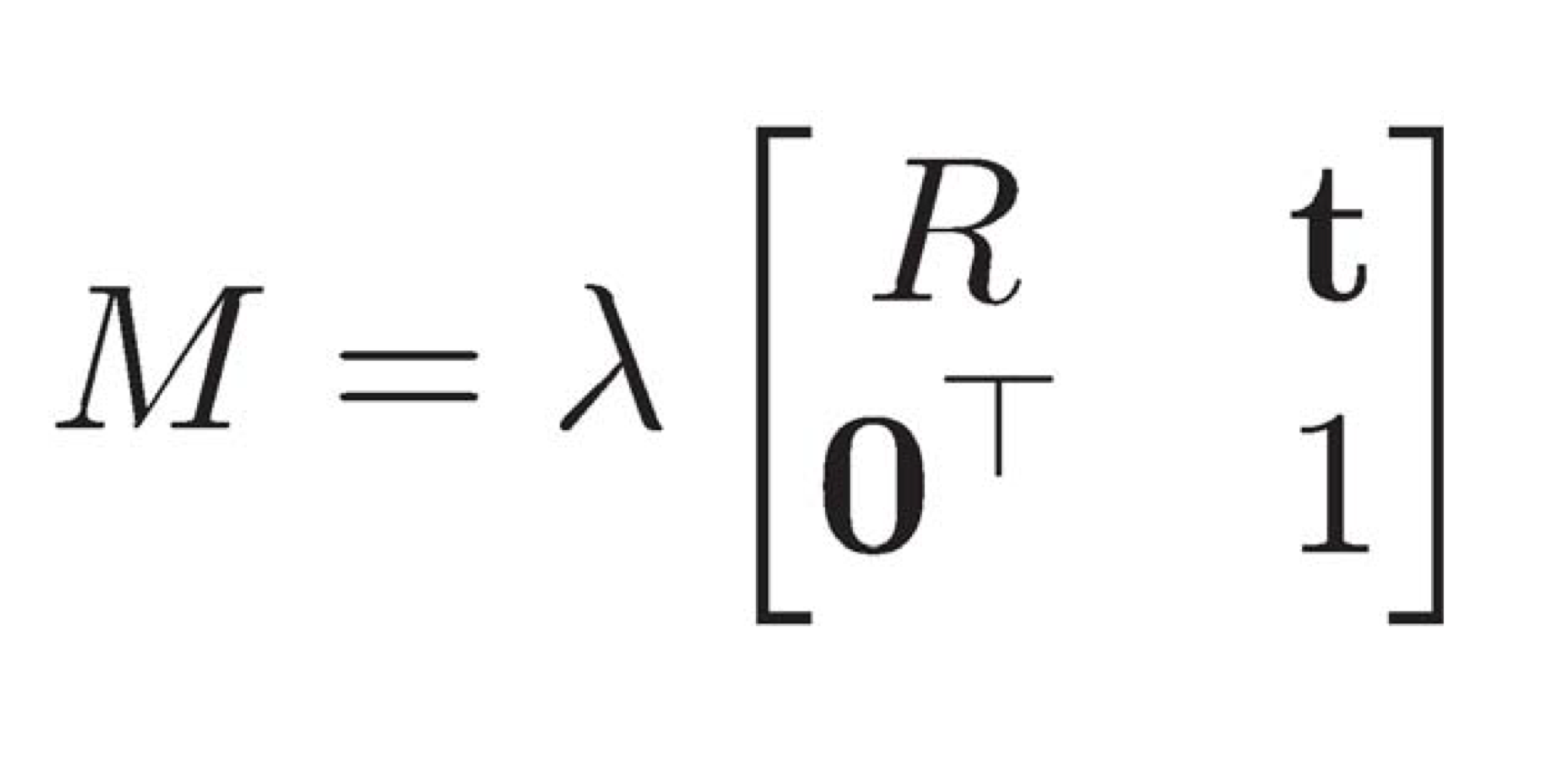
- Chaining tranformation via matrix
- x’ = M1M2x
14. Motion and Sensor Models
Recursive Bayes Filter
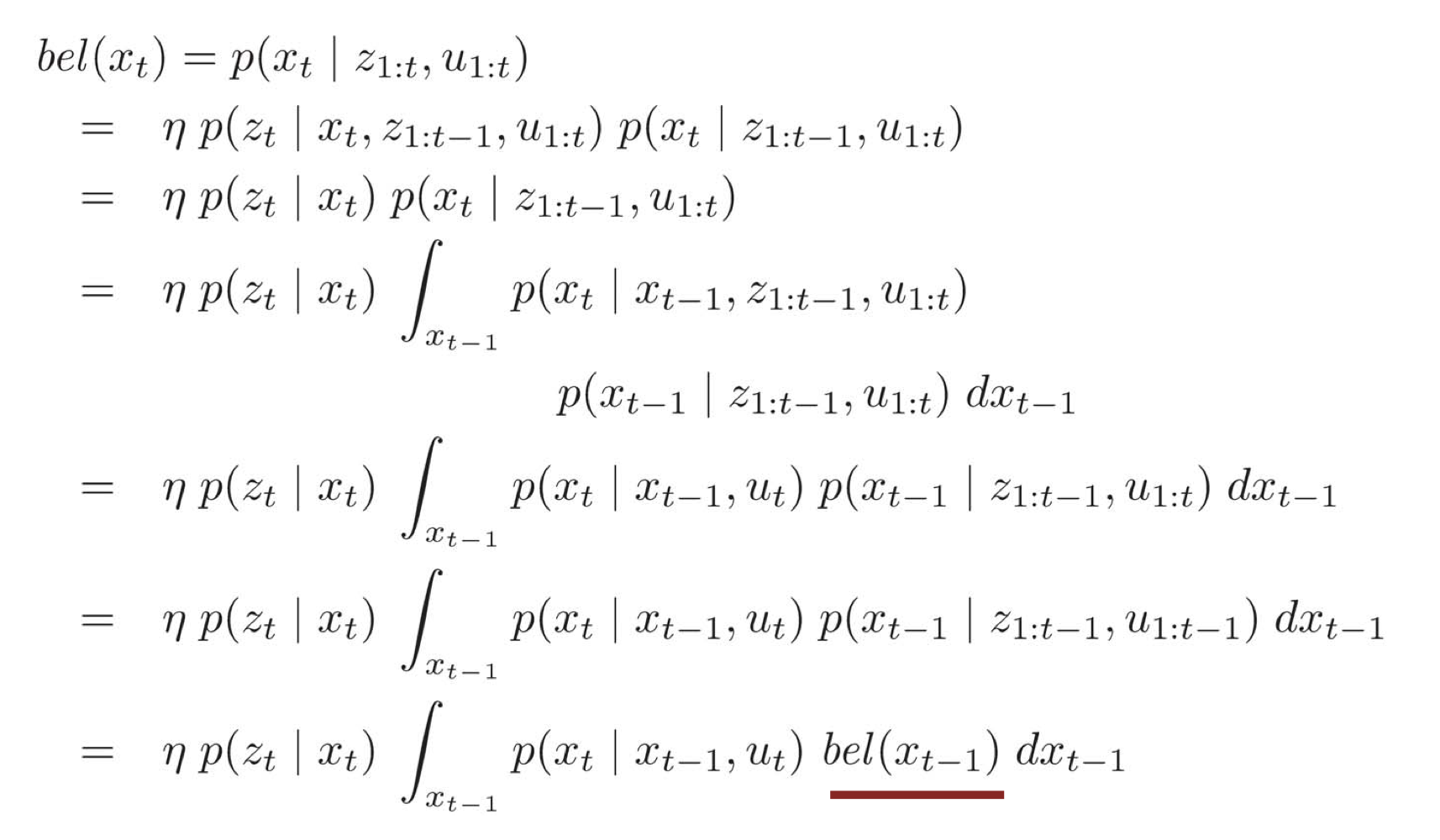
Prediction and Correction Step
- Prediction step

- Correction step
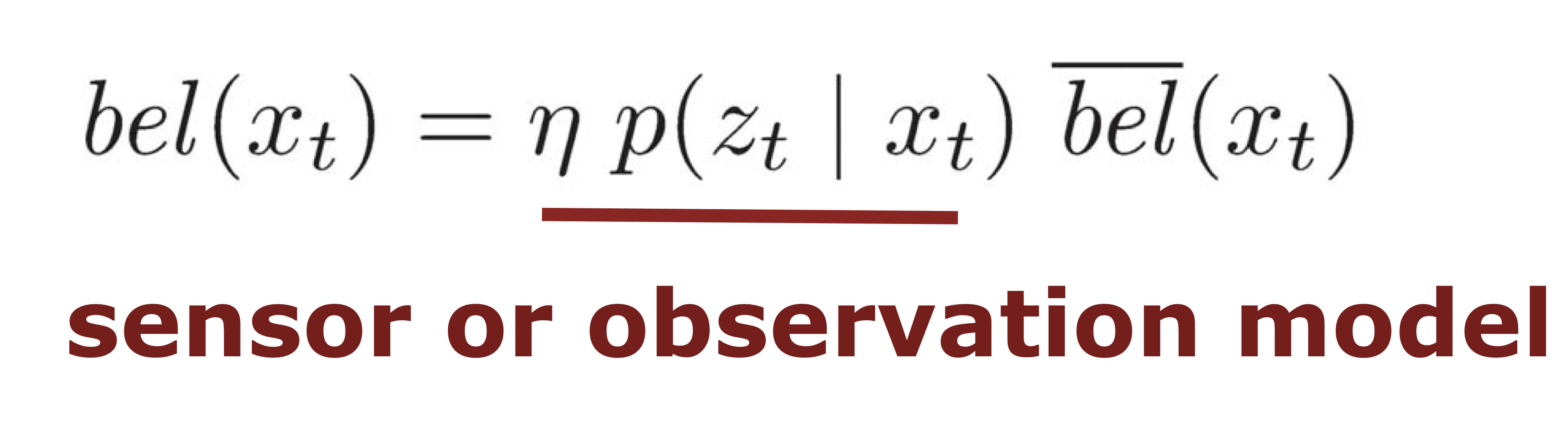
- Bayes filter는 recursive state estimation을 위한 framework.
- 다른 방식들을 사용한 다양한 filter들 존재.
Motion model
- 로봇의 모델은 불명확함.
- 두가지 방식의 motion model 존재
- Odometry-based
- wheel encoder가 있는 시스템을 위해 존재
- wheel encoder? 얼마의 힘을 주면 얼만큼 바퀴가 돌아가는지 계산하는 encoder
- Velocity-based
- wheel encoder가 없는 system을 위함
- 두가지 방법 중 Odometry-based가 더 정확.
- Odometry-based
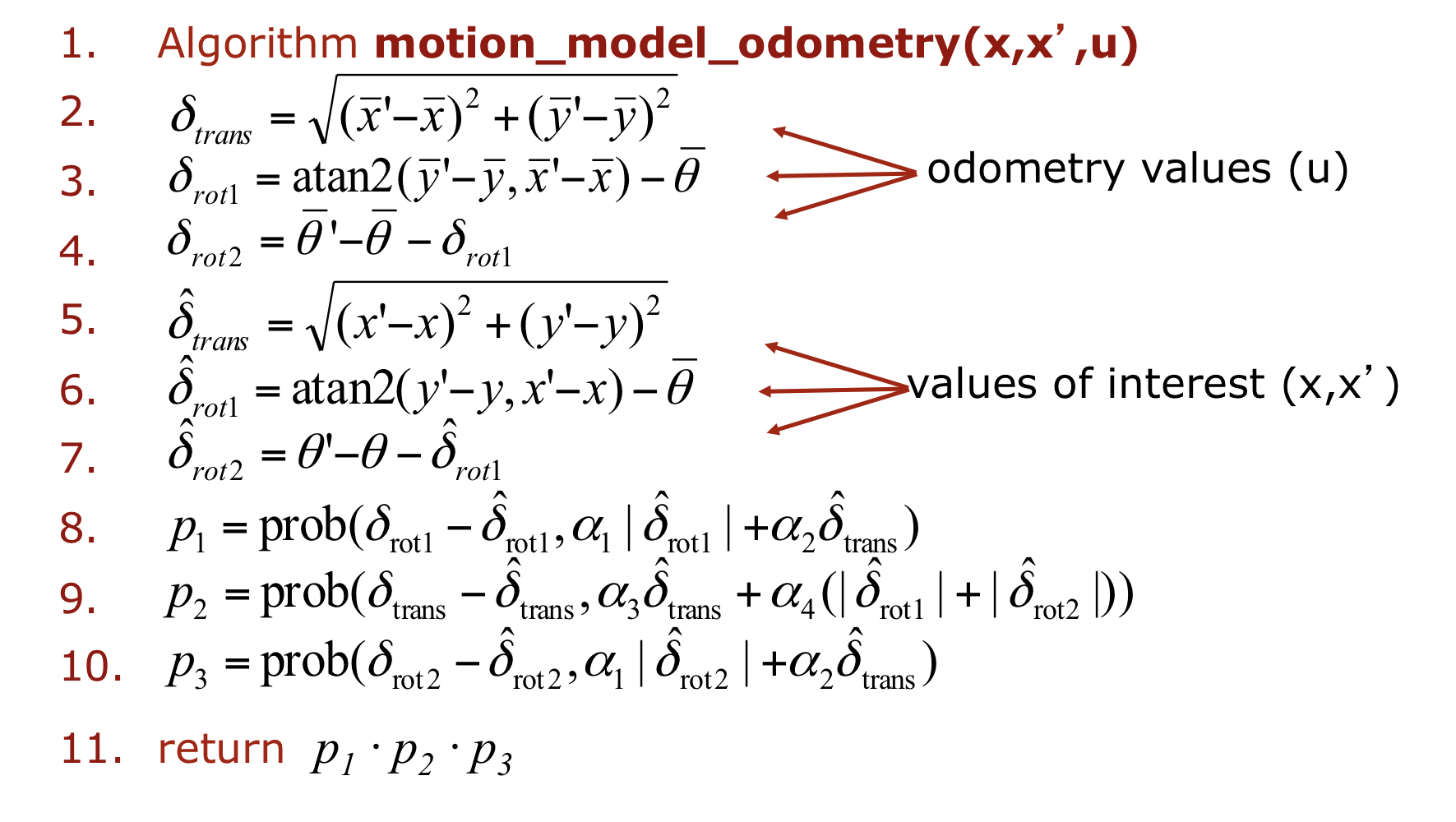
Odometry Model
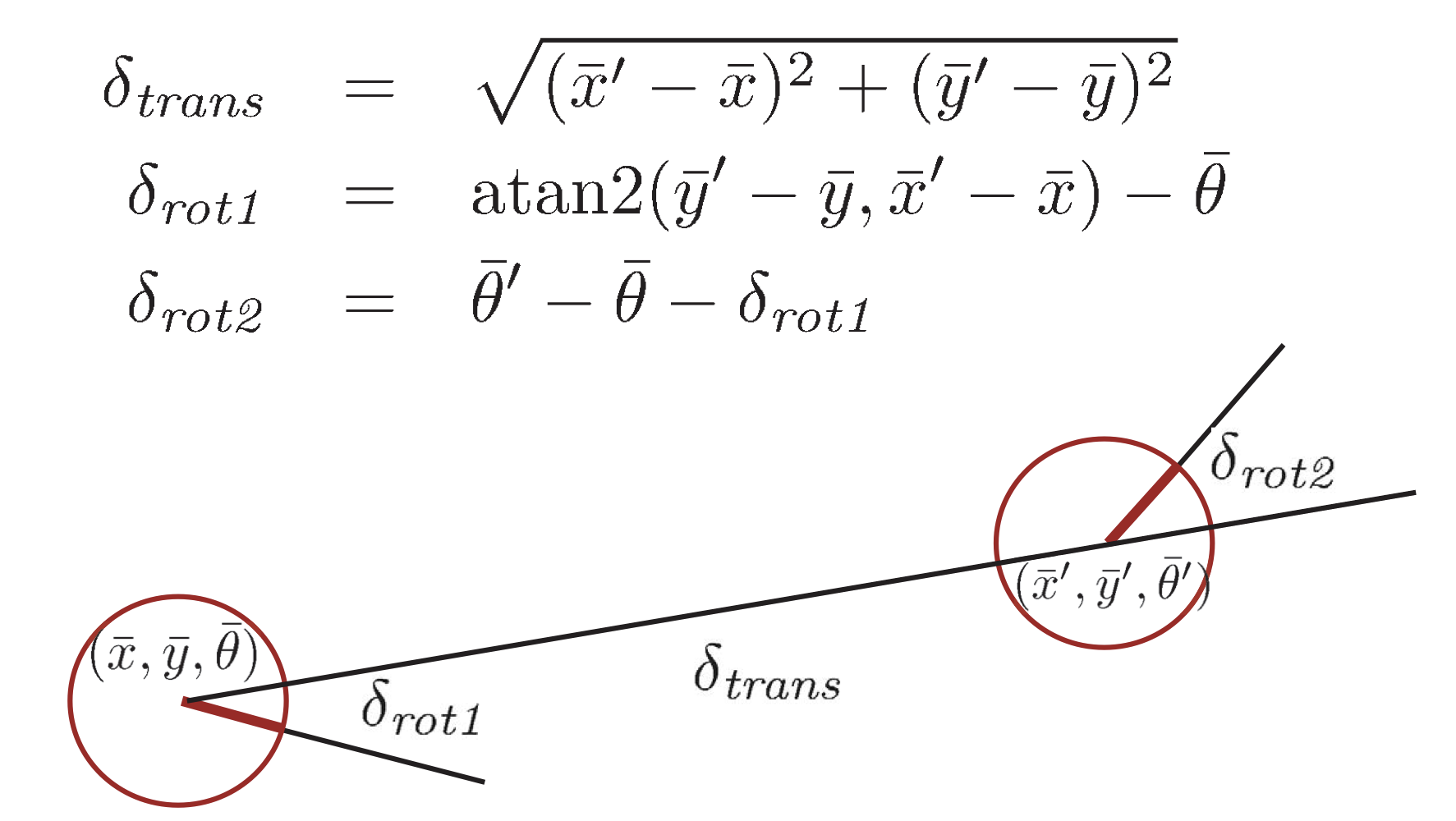
Robot motion
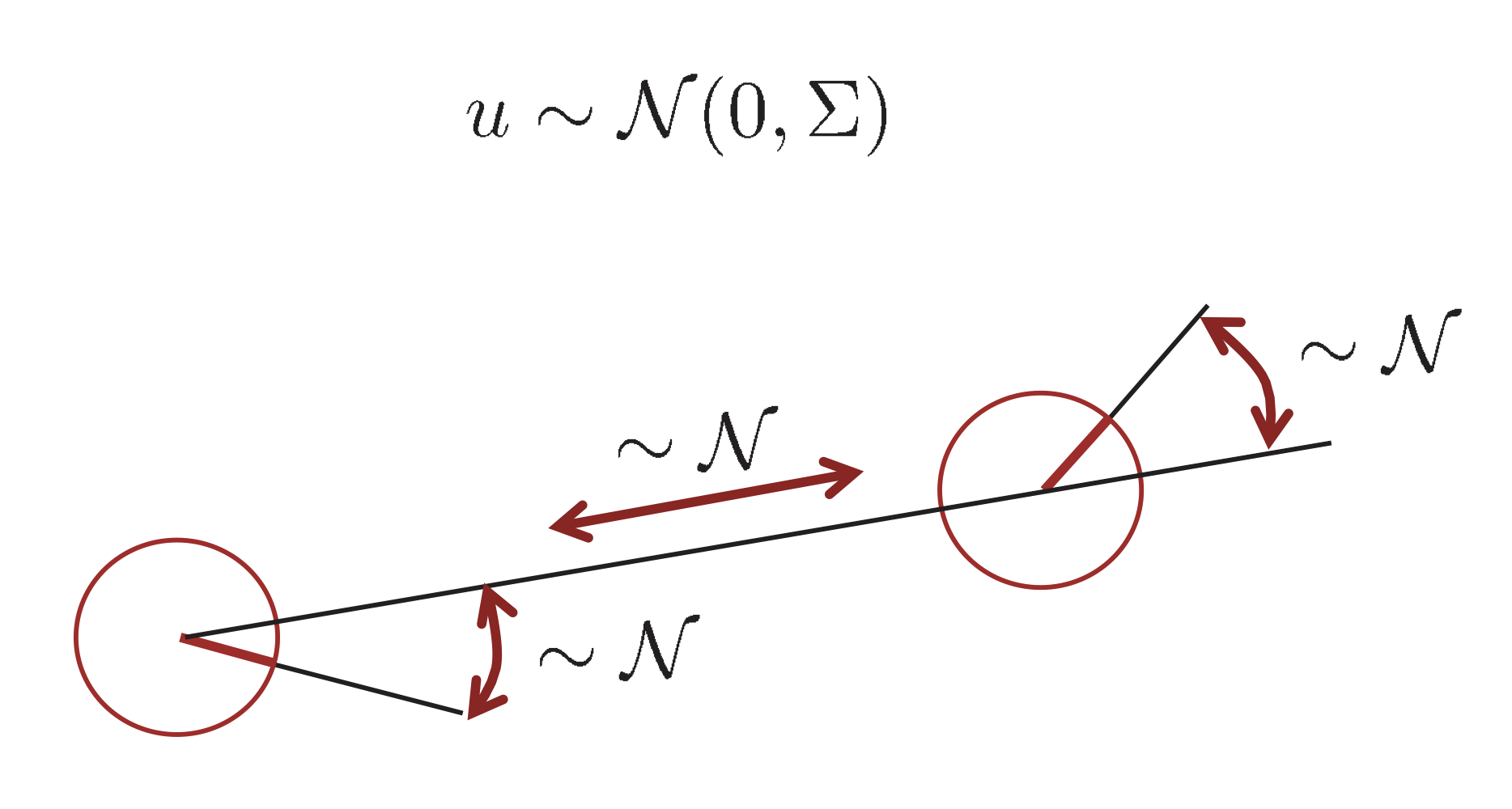
Noise
- Calculating the Posterior
Velocity-based Model
- Velocity-based Model은 로봇이 원을 그리며 지나간다고 생각을 하고, 이전 위치와 velocity를 이용하여 다음 위치를 구함.

- 이때 모델을 통해서 얻은 데이터은 서로 독립적이라고 가정.
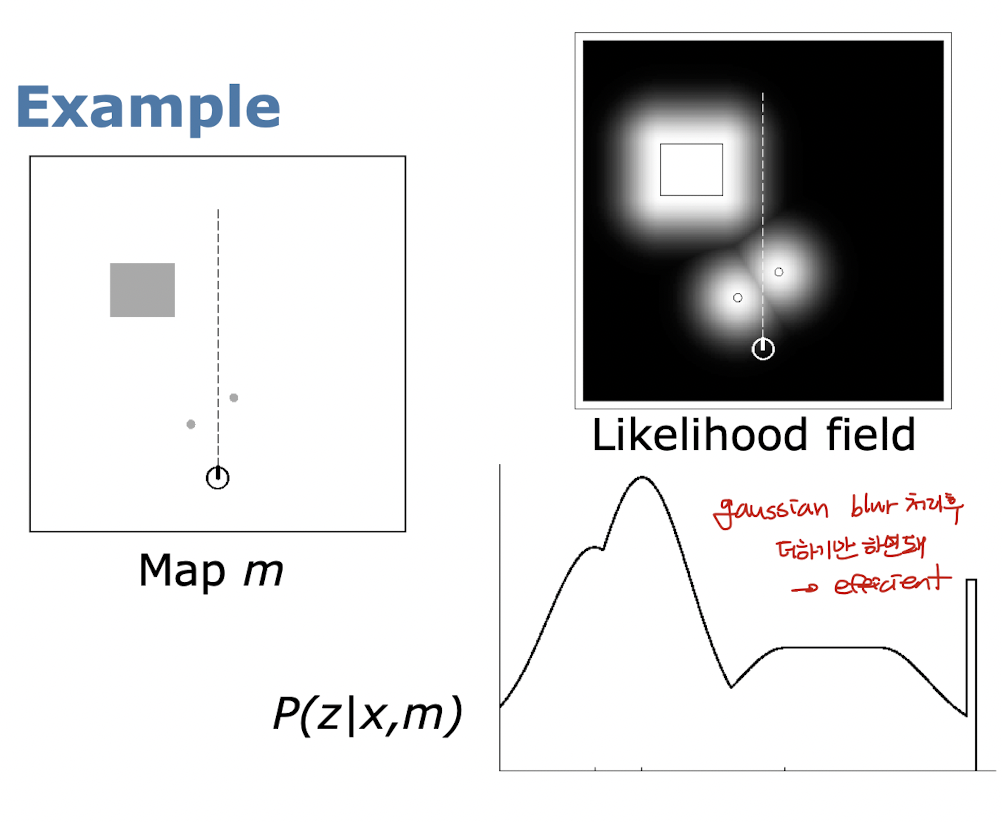
- Model for Laser Scanner
- Beam-based Sensor Model
- Beam-Endpoint Model
- Sensor가 측정한 값을 기준으로 Gaussian blur 처리.
- 이후 각 확률들을 더하기만 하면 되기 때문에 매우 efficient하다.
- Ray-cast Model
- Mixture of four models
- exponential distribution(Reflected by the obstacle) + gaussian distribution(Target) + uniform distribution(For random measurement) + pick distribution (For maximum measurement)
- Measurement error type
- Ray reflected by the obstacles
- Random measurment
- Maximum range measurement
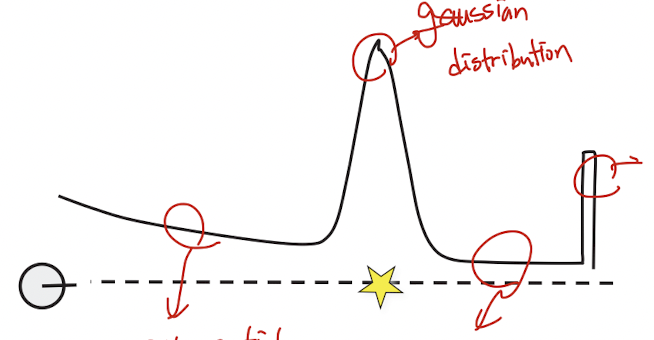
- Perceiving Landmarks with Range-Bearing Sensors
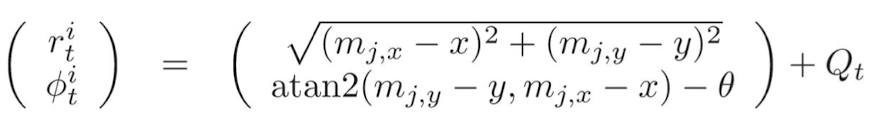
15. Kalman Filter
- Linear Gaussian distribution을 사용.
- 장점
- only need Mean and Variance
- 장점
Kalman Filter - 1D case
- Prediction
- Summation of Gaussian distribution
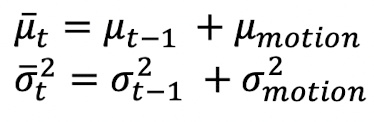
- Update
- 측정값의 평균, 분산과 예측값의 평균, 분산을 이용하여 최종값 update
- 평균을 구하는 방식은 분산이 더 작은 분포 쪽에 weight을 줄 수 있음.
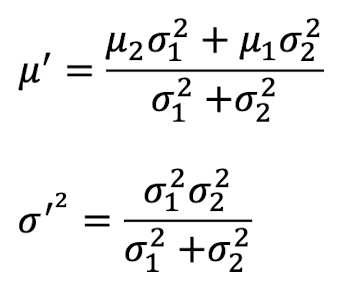
- Kalman gain
- 만약 mearsurement is more accurate, K = 1

Kalman filter - Multivariate
- Prediction
- 1D와 동일한 방식으로 진행.
- F: state transition matrix from state to state
- B: state transition matrix from control to state
- X and U matrix have different dimension → 맞춰줘야함
- Covariance 사용하여 prediction 진행
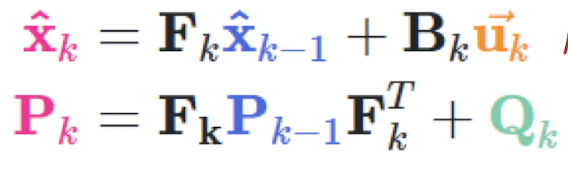
- Update
- 이떼 X는 predicted mean , H는 state transition matrix (using for synchronized dimension)
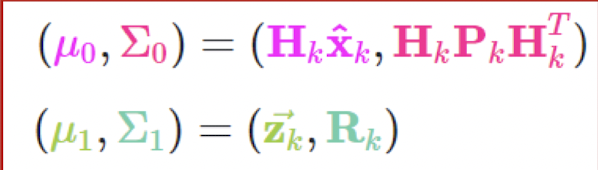
</figure>
<figure>
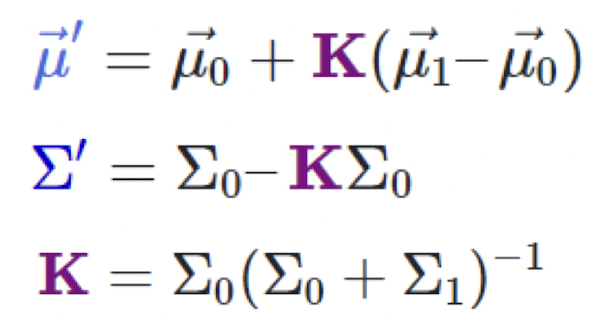
</figure>
- H 삭제. H는 dimension을 맞춰주기 위해 사용한 matrix이기 때문에 삭제 가능.
- 최종
<figure>
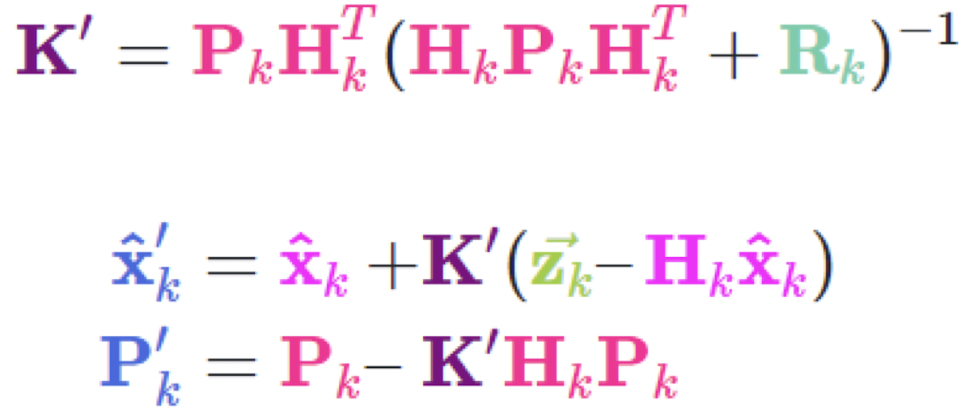
</figure>
Kalman Filter Assumption
- Kalman filter의 한계
- 모든 상황이 linear하다고 가정.
- 따라서 linear하지 않는 상황에서는 사용하지 못함.
- Gaussian distribution이 유지가 되지 않음.
16. Extended Kalman Filter
Kalman Filter Problem
- linear하지 상황에서 transformation을 하게 되면, 더이상 Gaussian Distribution이 아니게 된다. 따라서 이를 더이상 mean과 variance만을 이용하여 구할 수 없음.
- 하지만, 대부분 실제 상황에서는 nonlinear한 함수이다. 따라서 Kalman Filter를 사용할 수 없음.
- 이를 해결하기 위해 Local linearization을 사용.
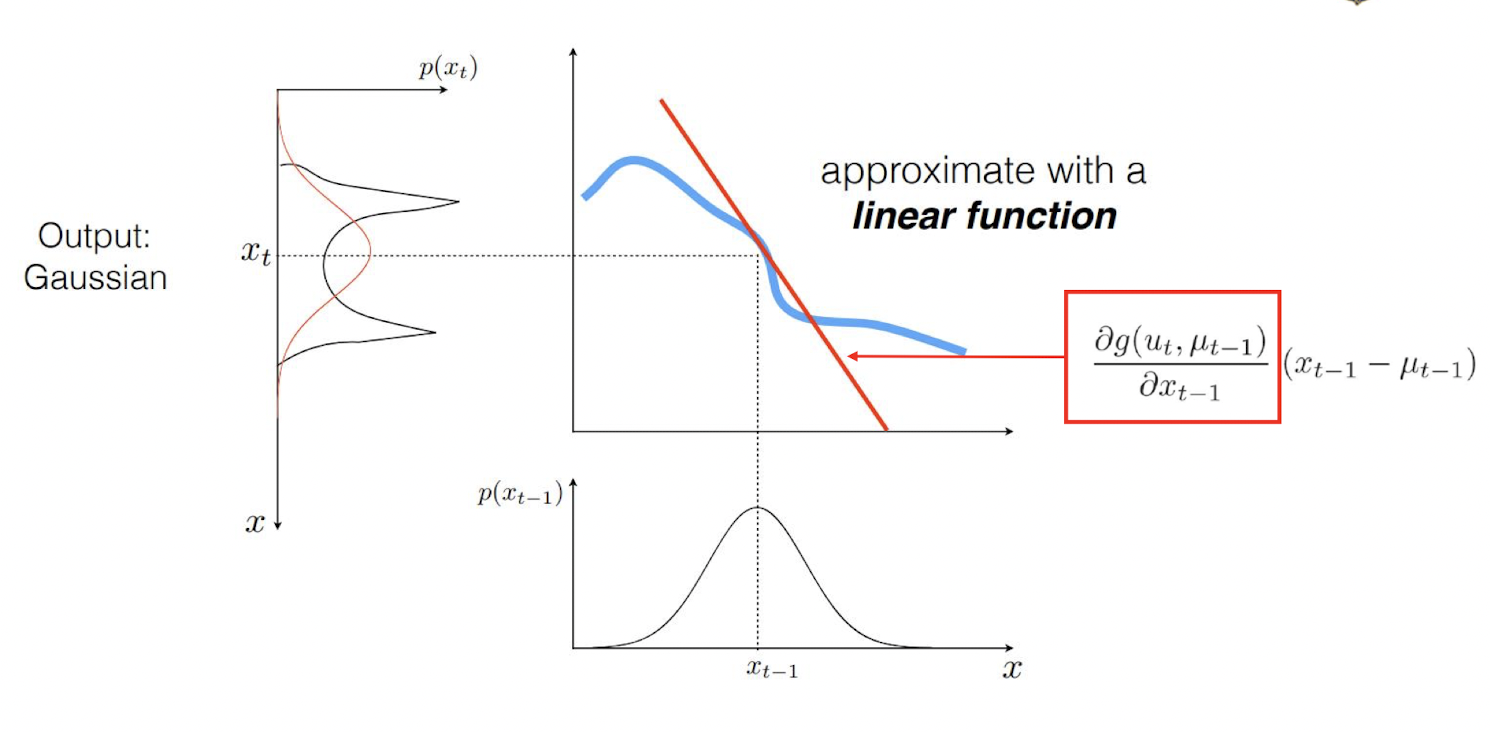
Non-linear transformation
- Non-linear한 상황에서, 특정 부분은, linear transformation으로 approximate할 수 있음.
-
Taylor series를 이용하여 특정 부분을 linearization함.
를 이용.
EKF Linearization - First order Taylor Expansion
- Prediction
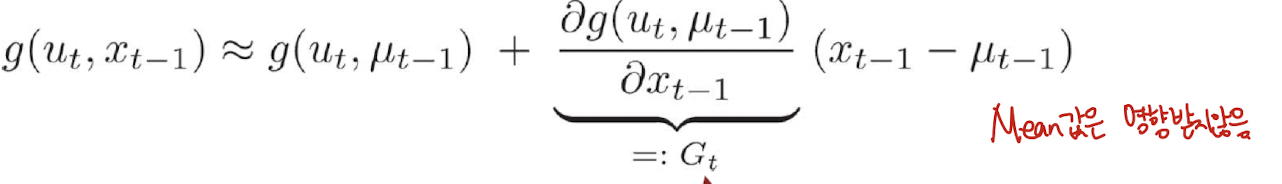
- Correction
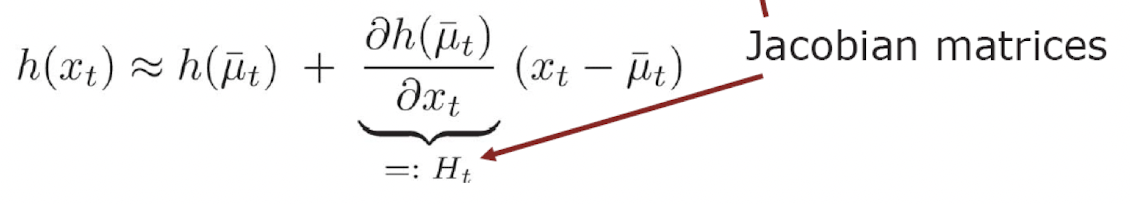
- Kalman Filter vs Extended Kalman Filter


17. EKF SLAM
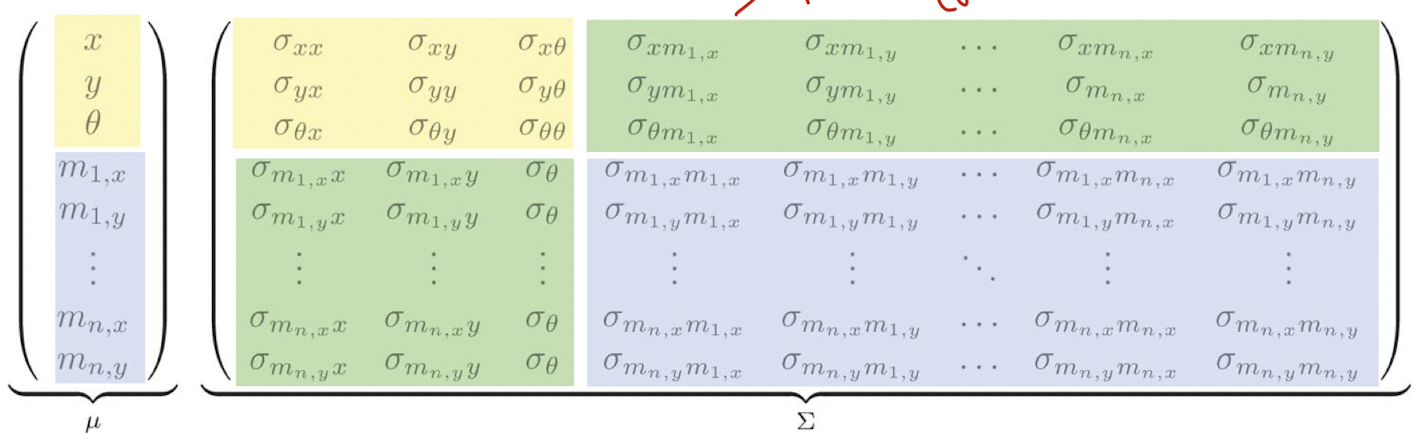
EKF SLAM
- State space for the 2D plane constructed with robot’s pose and landmarks
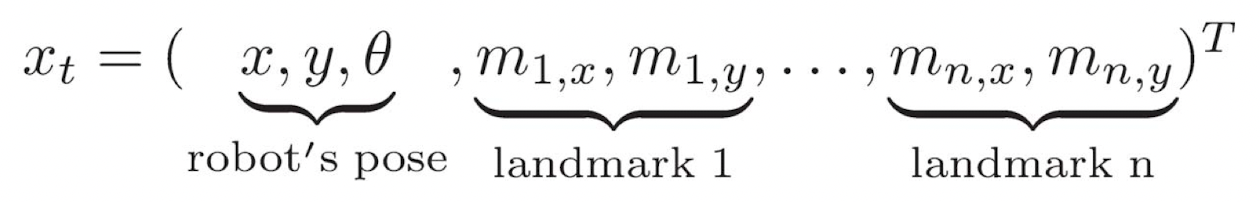
- Mean and Variance
- Filter Cycle
- Initialization
- Robot은 자신만의 reference frame이 존재 (주로 처음 시작 frame이 reference frame) 이때 모든 Land mark는 모르기 때문에, 0으로 초기화
-
Variance의 경우, 처음 위치는 불확실성이 없어 무조건 0, 반대로 landmark에 대해서는 불확실성이 매우 높기 때문에 무한대로 초기화 해줌(해당 값을 사용하지 않겠다는 뜻)

- Memory consumpotion: O(n^2)
18. Particle Filters and Monte Carlo Localization
Particle Filter
- Particle Filter는 이미 Map을 아는 상태에서 진행.
- Recursive Bayes filter
- Non-parametric approach
- Key Idea: Sampling
- 임의의 분포를 여러개의 samples을 통해 나타낸다.
- Particle Set
-
Set of weighted samples
를 구했을 때 C보다 큰 샘플들만 모았을때 나온 결과는 분산을 대변.
- 임의의 값 C 지정
- Importance Sampling Principle
- Gaussian distribution의 경우, 다음과 같은 식을 이용하여 분산에 맞는 샘플을 얻을 수 있음. 하지만, 임의의 분산의 경우에는 이러한 식을 구하는 방법이 어려움.
- 이때에는 분산의 차이를 이용하여 진행. 즉, proposal 분산에 대한 sample을 우선 먼저 추출. 이후 각 가중치를 이용하여 해당 샘플이 target 분포와 맞는 sample이 될 수 있도록 한다.

Resampling
- 가장 그럴듯한 샘플들만 남겨 가능성이 적은 Particle은 제거.
- 크게 2가지 방식 존재
- Roulette wheel
- 각 Weight를 normalize한 후, Binary search를 통해 진행.
- 한번의 1개씩 random하게 particle을 추출한다.
- 따라서 시행할 때마다 다르므로 Variance 큼.
- O(J log J)
- Stochastic universal sampling
- Low variance
- O(J)
- 화살표를 돌리면서 그때마다 화살표에 해당하는 W을 가지고 있는 Particle만 채택
- Roulette wheel

19. Fast SLAM
Dimensionality Problem
- Particle Filter는 low dimension에서 효과있음.
- 실제 SLAM은 High-dimension
- 따라서 Particle filter를 SLAM에서 사용하기 위해 로봇의 Pose에만 Particle Filter를 적용. Map은 EKF를 사용하여 로봇의 trajectory estimation으로 사용. 즉, 각각의 Particle마다 Map을 예측하고, Observation과 비교하며 진행.
Rao-Blackwellization

FastSLAM
- 각각의 Particle은 각각의 Landmark에 대한 EKF를 가지고 있음.
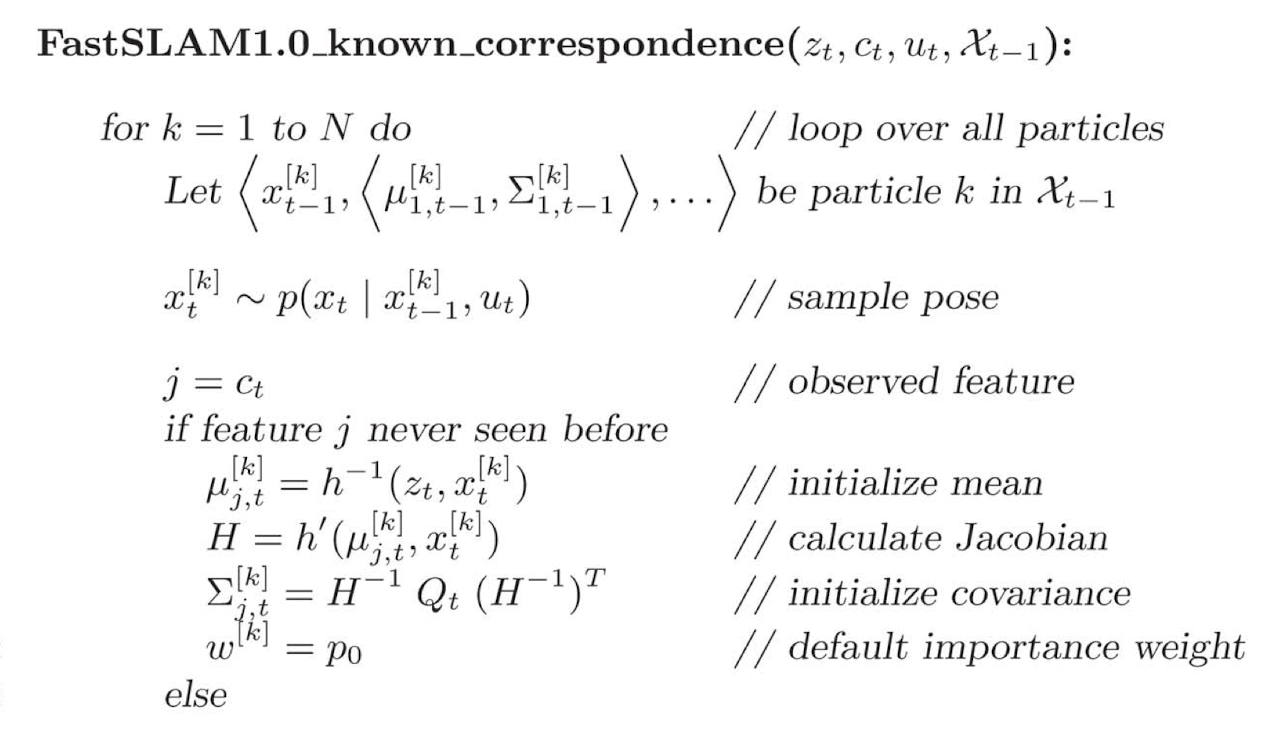
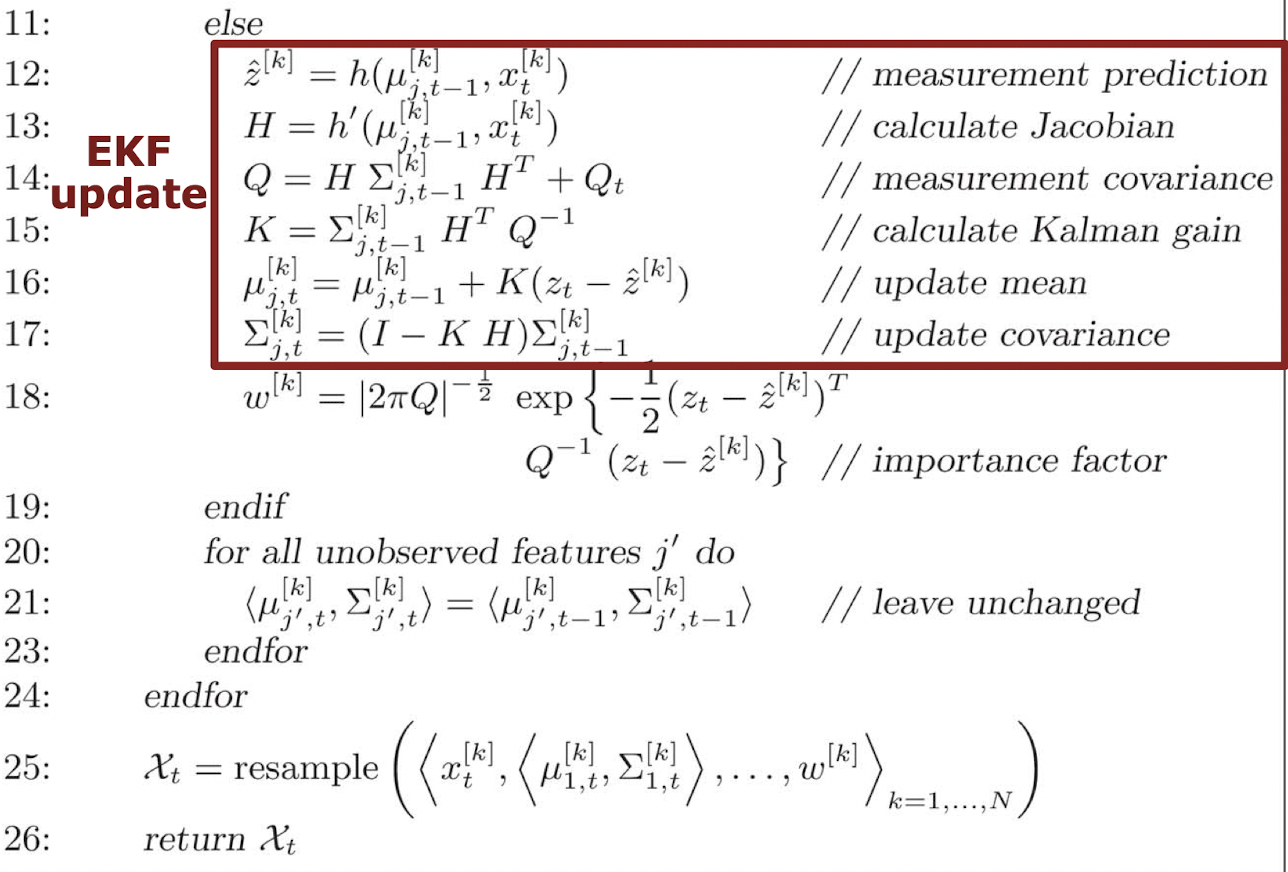
Short version

Long version
20. Occupancy Grid Maps
Logit
- 언제나 확률분포로 변환 가능하게 하는 함수, log(odds)
- Odds : P/not P
Grid Maps
- Map을 grid로 나누는 것.
- 각 cell은 occupied인지 free space인지 판단.
- Non-parametric
- Assumption
- The area either free or occupied
- binary random variable
- World is static
- The cells are independent (계산상의 편의를 위해)
-
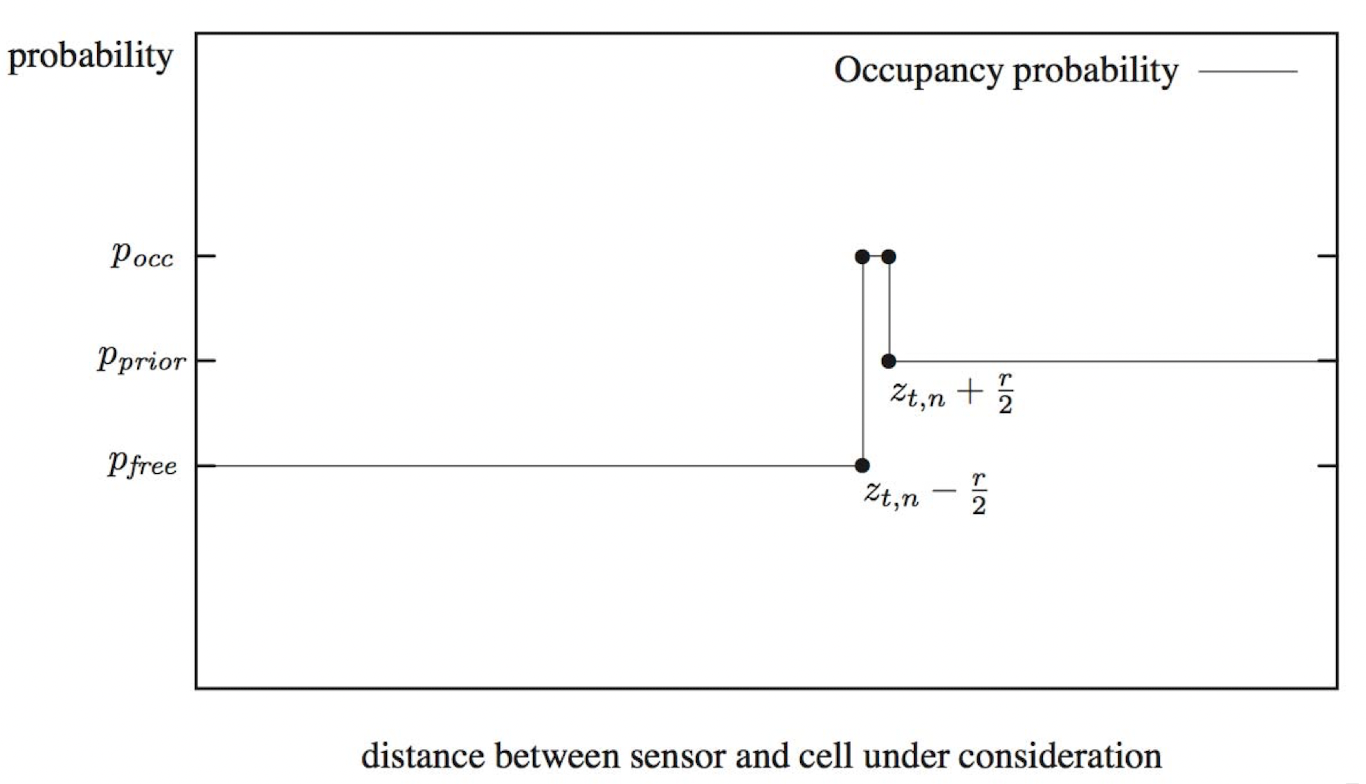
Occupancy Probabilities
 계산.
를 구할 수 있음.

- Lidar는 sonar에 비해 거리측정 오차가 매우 적다. 따라서 occupied로 생각하는 영역이 sonar모델에 비해 매우 좁다.4
- Sonar Sensor model
- 로봇의 위치와 센서 관측값이 있을 때 각 cell의 occupied 되어 있을 확률이다. 여기서는 2가지 모델을 예를 보여준다.
Sonar Sensor
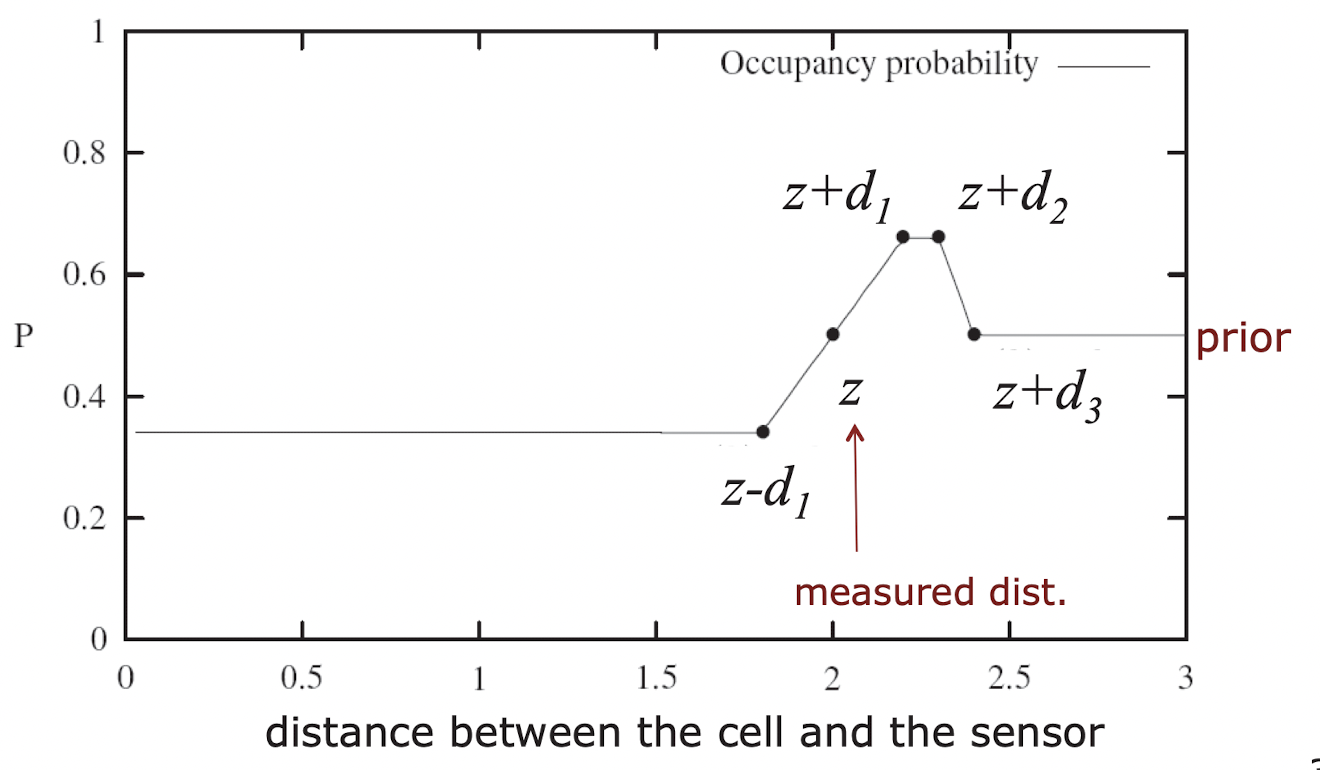
Laser Range Finder
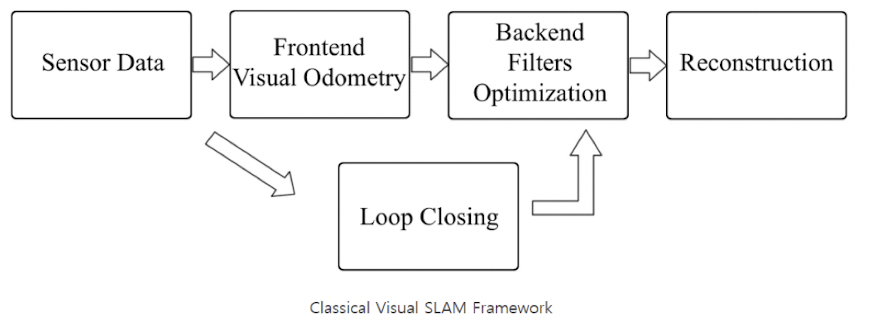
22. Visual SLAM
Building and Tracking a map
- Building
- Tracking
- Point correspondences를 통해 pose 구함.
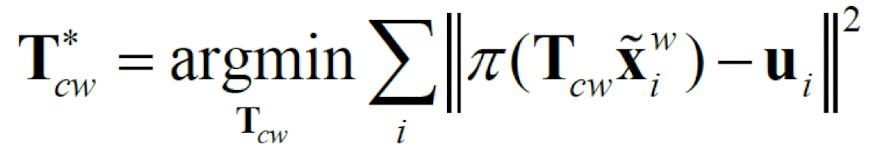
Component of Visual SLAM
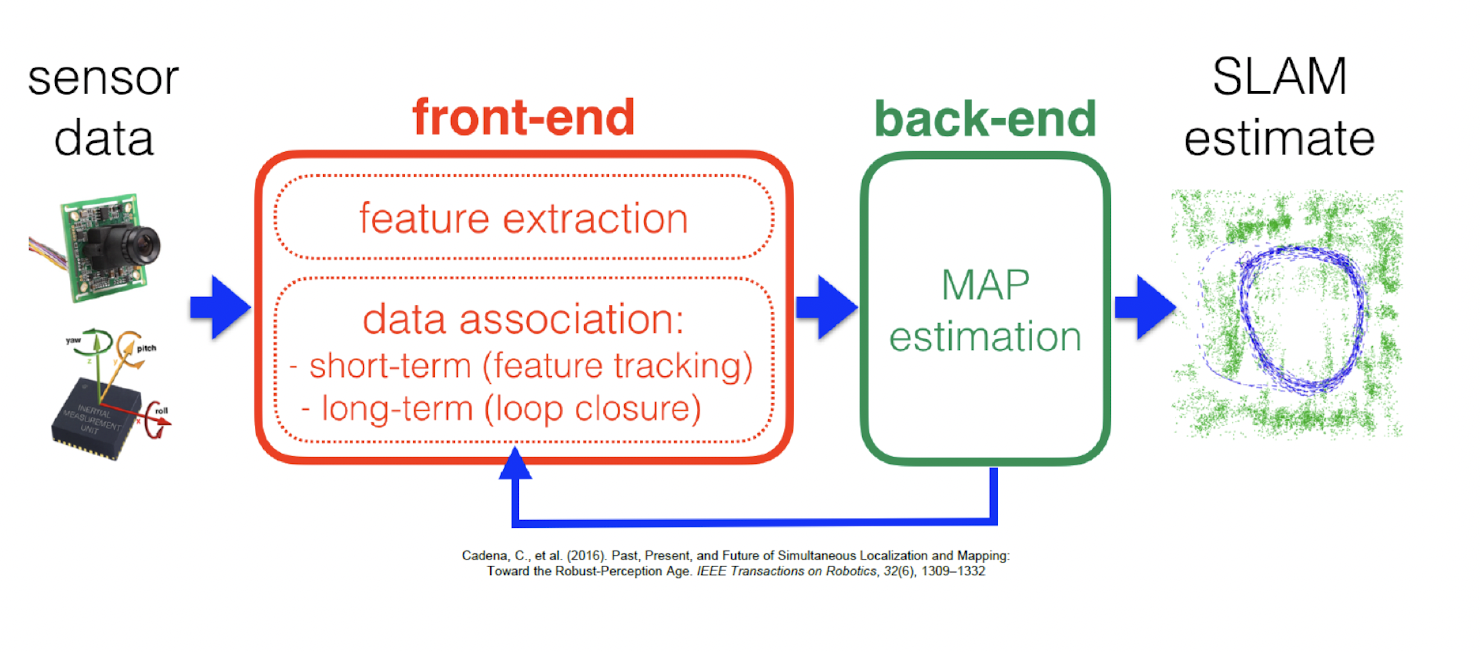
- Short-term tracking
- Pose estimation given the map
- Keyframe proposals
- Long-term tracking
- Visual place recognition
- Loop closure detection over keyframes
- Mapping
- Building and optimizing the map over keyfrrames
- Data fusion
Local Features
- 주변과 다르게 특징이 되는 이미지 feature
- Saliency, Locality
Feature detection
- Corners, Blob regions
- Conrner
- 모든 방향에서 변화가 일어남.
-
Gradient를 이용하여 Corner 찾음.

- 엣지부분에서 위아래 변화. 일정 부분 이하로 두 엣지 사이가 가까워지면 (blob) 값 중첩되어 커짐., 블록의 크기 정해져있음. 동일 커널로 이미지 크기 다양하게 하여 찾음.
- 이미지에 blob이 많고, 해당 kernel 에 걸리는 blob을 찾고싶을 때 kernel 고정
- 반대의경우에는 kernel을 여러개 사용하거나, 아님 이미지의 크기를 여러개 사용하여 kernel을 여러개 사용하는 방식과 동일하게 사용할 수 있도록 함
- DOG
- 가우시안의 차를 이용하여 계산(SIFT에서 사용)
- 이미지 blur 4번 한 것이 이미지 크기를 줄인 것과 동일. 따라서 이미지를 줄여서 사용. → 계산량 감소
- LoG(Laplacian of Gaussian)
- Point detector
- FAST
- 가운데 점을 중심으로 원을 16개 점 → 연속해서 12개의 점이 밝을 경우 코너로 정의.
- FAST
Feature descriptor
- Template: N*N image patch를 이용, Descriptor: 주로 Vetor를 이용하여 표현.
- Template matching
- SAD
-
difference 값이 작을수로 matching. (절대값)


- HOG와 비슷하게 grandient vector를 구한 후, 4*4 window에 8개의 direction으로 vector 합쳐줌.
-
pick point를 기준으로 돌림. 이후 HOG와 비슷하게 gradient vector 구함. tree 형식으로 매칭.

Prerequisite
- Covisibility graph
- 각 keyframe들이 edge로 연결되어 있는 그래프.
- 각 edge의 weight은 각 Keyframe에서 겹치는 Key point들을 나타냄.
- Essantial graph
- Minimal spanning tree (최소신장트리) 가장 연결이 많이 되는 Keyframe들만 사용.
- Bag of words
- code → clustered descriptor (dimension을 나눌 때 cluster 되어있는 부분)
- code book → 각 code를 histogram으로 표현.
- 즉 해당 scen에 대한 descriptor
- Perspective n Point
- n : 2D to 3D일때 사용된 점의 개수
- 2D를 넣으면 3D pose 나옴. (translation & rotation)
- Camera coordinate 에 대한 World coordinate (지정 좌표계)
- Bundle Adjustment
- pixel → world point 구한후, 이를 다시 projection하여 최적화.
- intrinsic parameter , pose, point 보정
Place Recognition
- Visual vocabulary와 Recognition Database (Codebooks of keyframes)를 이용하여 Place recognition 진행.
Tracking
- Feature extraction
- 256 bit descriptor
- Harris corner로 candidate pixel extract, 이것들로 진행
- Pose estimation
- Homography → 평면간의 matrix
- Fundamental Matrix → 3D planar scene matrix
- Relocalization
- Track Local Map
- pose에 대해서만 bundle adjustment 진행.
- New Keyframe Decision
Local Mapping
- Recent Map Point Clustering
- New Map Point creation
- Local BA: 3D map, pose 둘다 adjustment 진행 전체를 하는것이 아닌 주변 연결된 몇개의 keyframe 간의 optimize 진행.
- Local keyframe culling: keyframe culling 진행. (90% map points are visible in 3 other keyframes)
Loop Closing
- Loop Detection
- Loop Correction